"Inter-target" communication
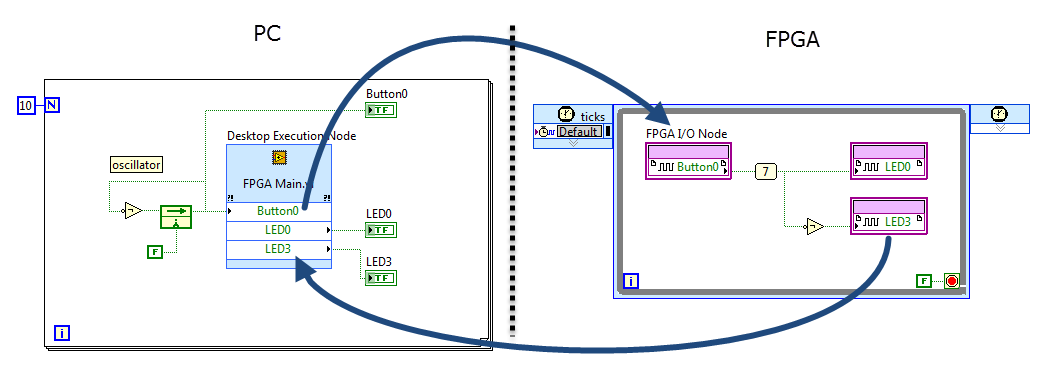
"Desktop Execution" node as an FPGA VI testbench
FPGA code PC code
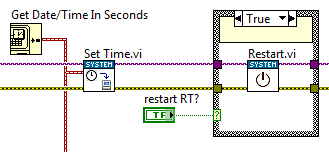
Set RT system time/date from PC
RT code PC code
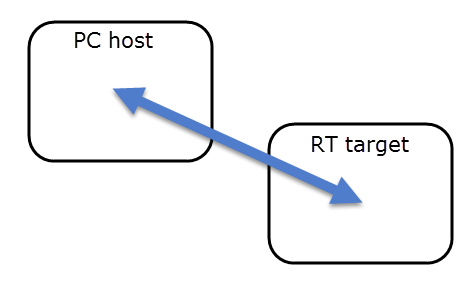
RT/host inter-target communication
RT guide PC guide
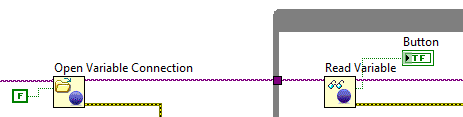
Programmatic front-panel communication with RT
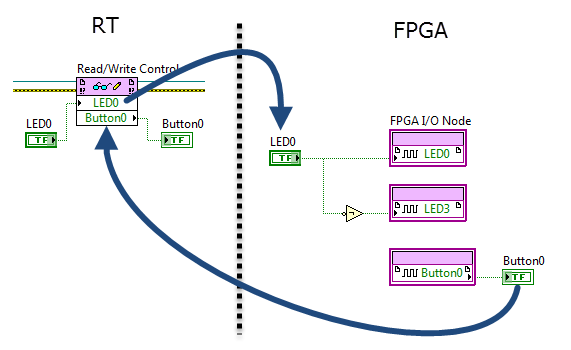
FPGA code RT code
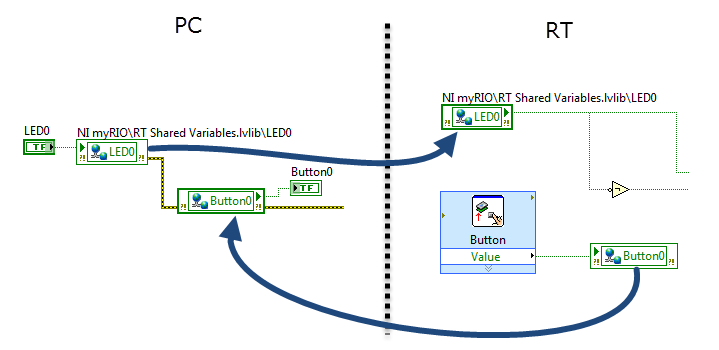
Create a network-published shared variable (NPSV)
RT procedure PC procedure
Bind a PC VI front-panel indicator to a network-published shared variable (NPSV)
RT procedure PC procedure
Network-published shared variable (NPSV)
RT code PC code
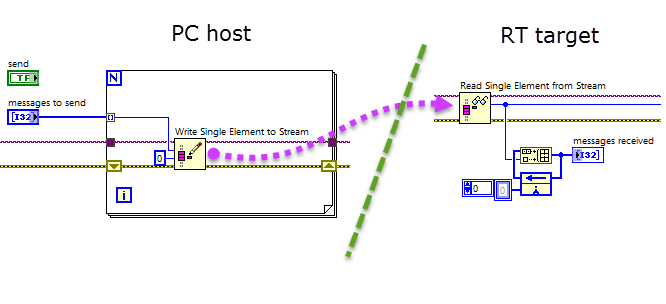
Send messages through a network stream channel
RT code PC code
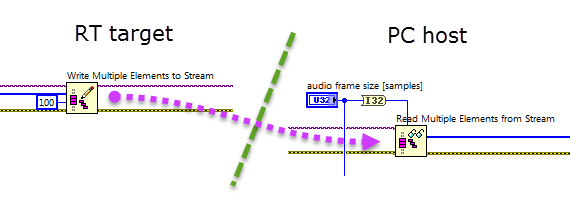
Stream high-speed data through a network stream channel
RT code PC code
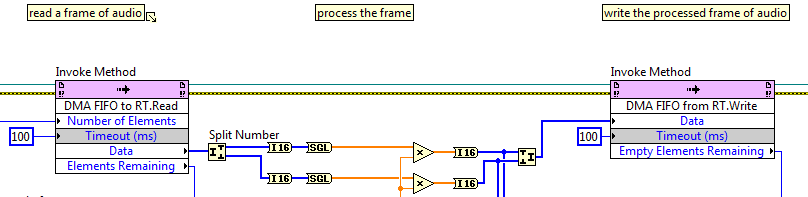
Stream high-speed data between FPGA and RT with a DMA FIFO
FPGA code RT code
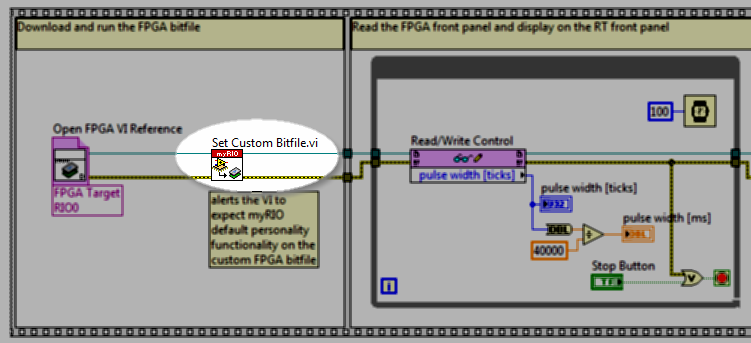
Augmented default Academic RIO Device FPGA personality and high-precision waveform measurement application example
FPGA code RT code
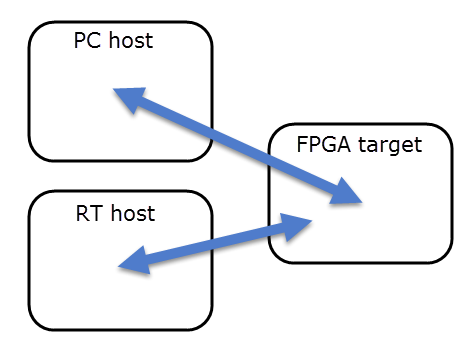
FPGA/RT and FPGA/host inter-target communication
FPGA guide RT guide PC guide
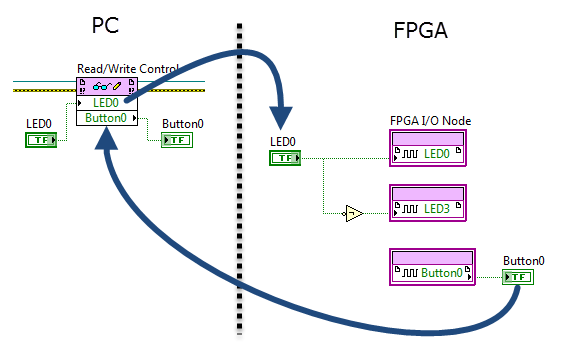
Programmatic front-panel communication with PC
FPGA code PC code
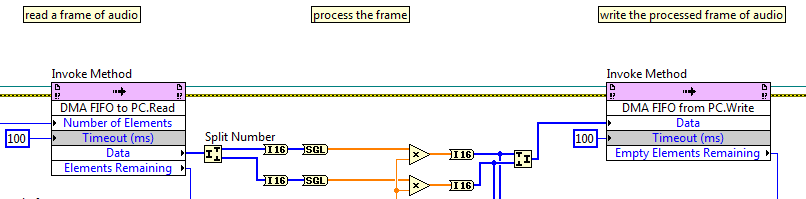
Stream high-speed data between FPGA and PC with a DMA FIFO
FPGA code PC code
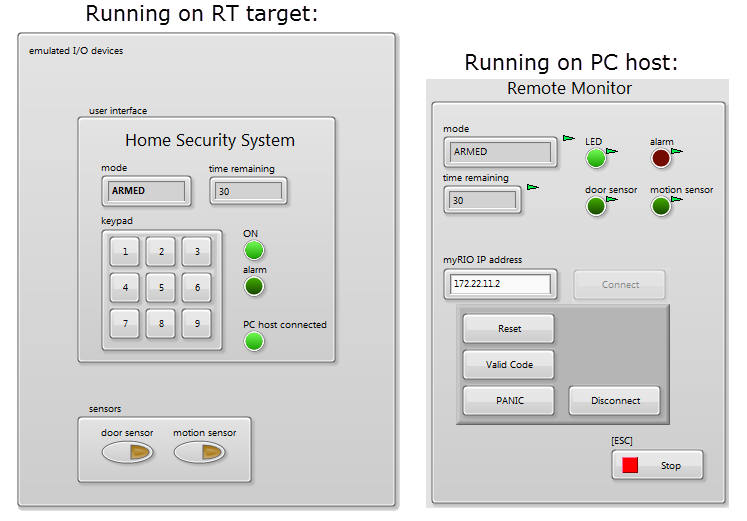
System controller application example: Home Security System
RT code PC code