"Tag" communication
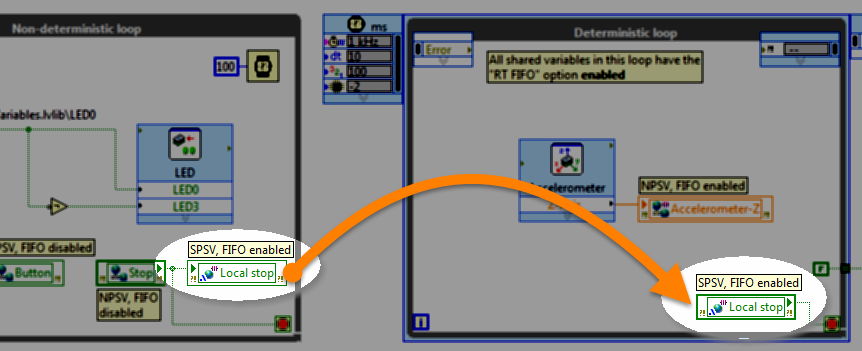
Local variable (RT)
RT code
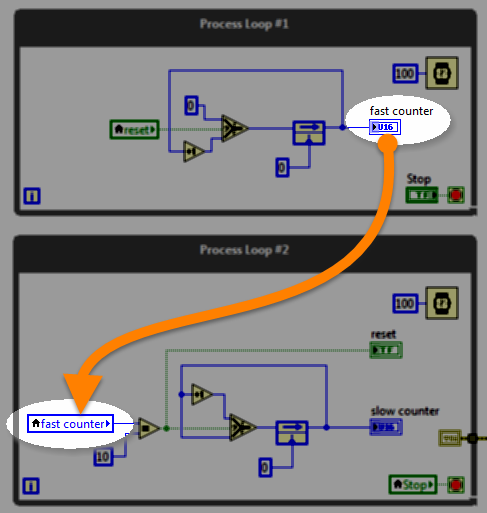
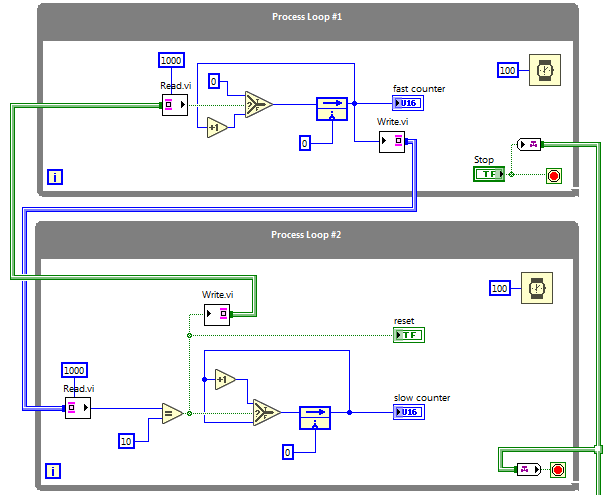
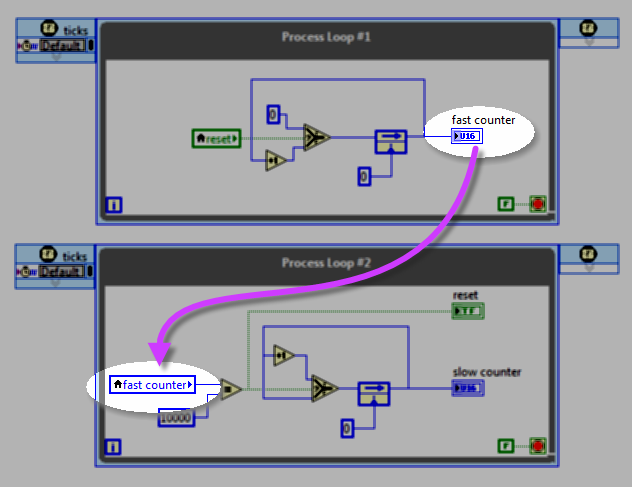
Global variable (RT)
RT code
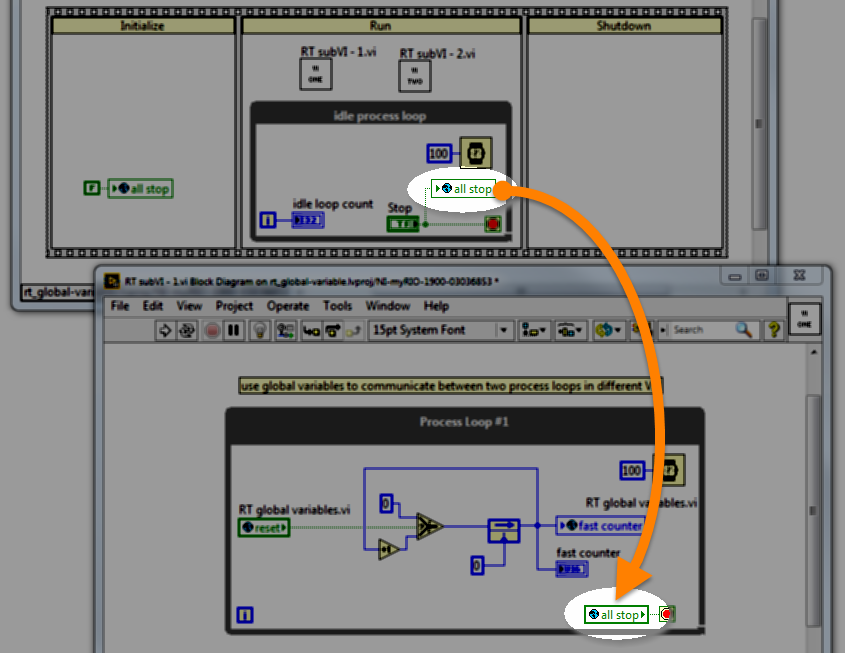
Functional global variable (FGV)
RT code
Channel wire
RT code
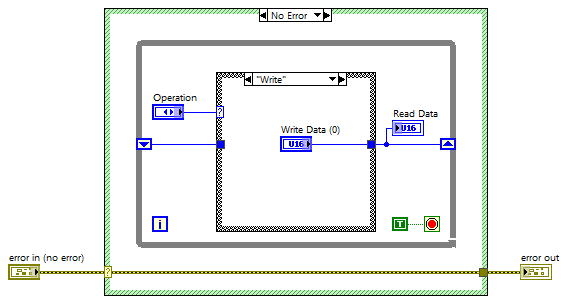
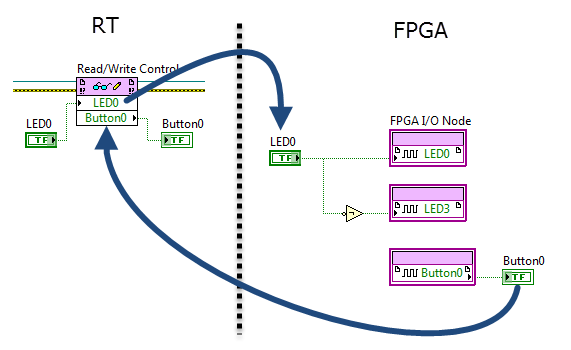
Local variable (FPGA)
FPGA code
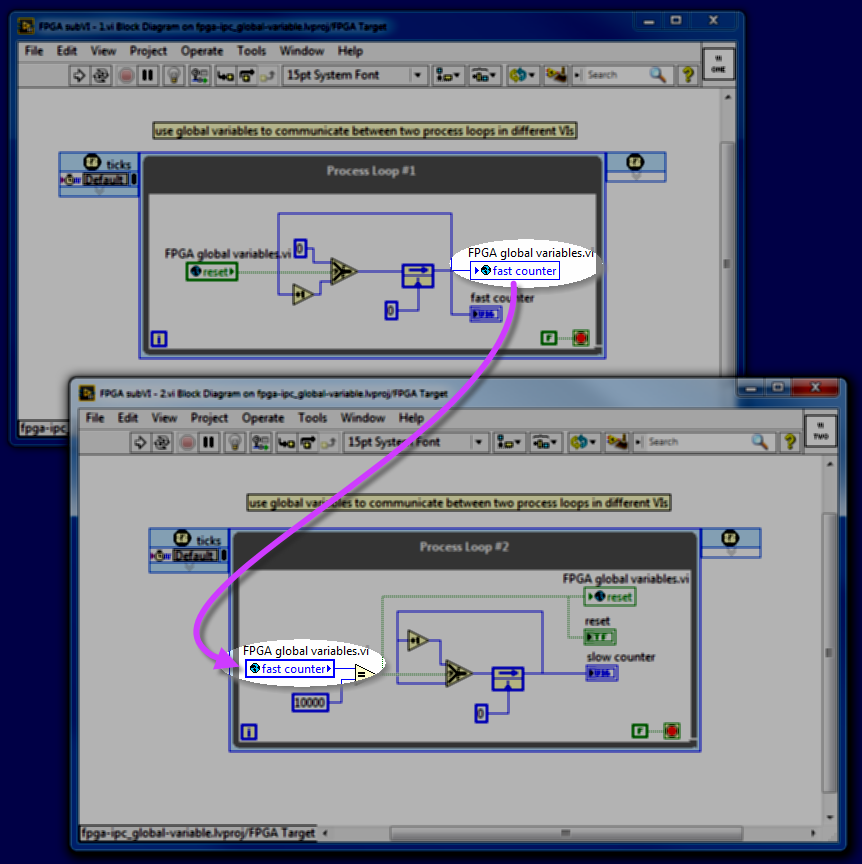
Global variable (FPGA)
FPGA code
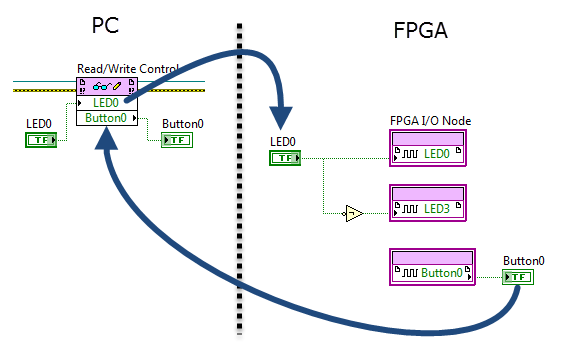
Programmatic front-panel communication with RT
FPGA code RT code
Create a network-published shared variable (NPSV)
RT procedure PC procedure
Bind a PC VI front-panel indicator to a network-published shared variable (NPSV)
RT procedure PC procedure
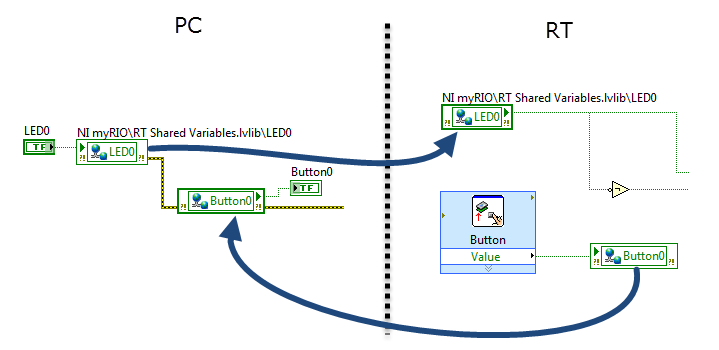
Network-published shared variable (NPSV)
RT code PC code
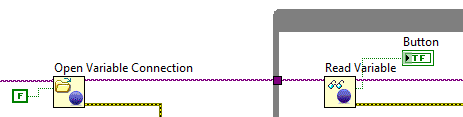
Programmatic front-panel communication with PC
FPGA code PC code
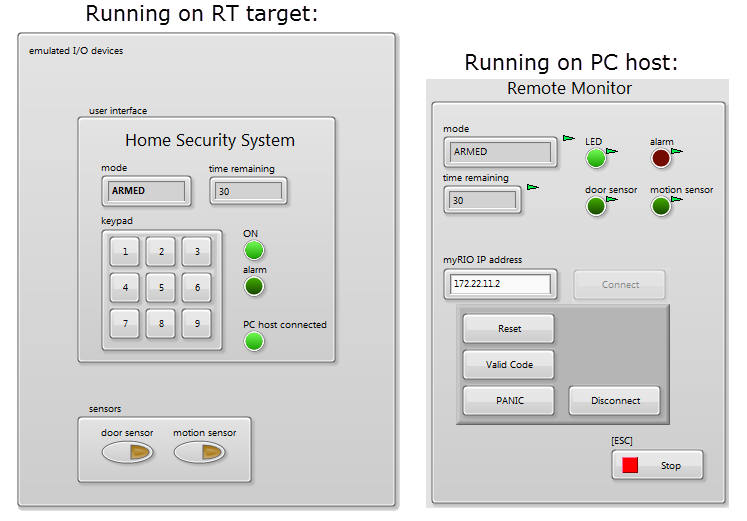
System controller application example: Home Security System
RT code PC code