RIO Developer Essentials Guide for Academia
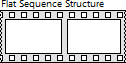
"Flat Sequence Structure" element
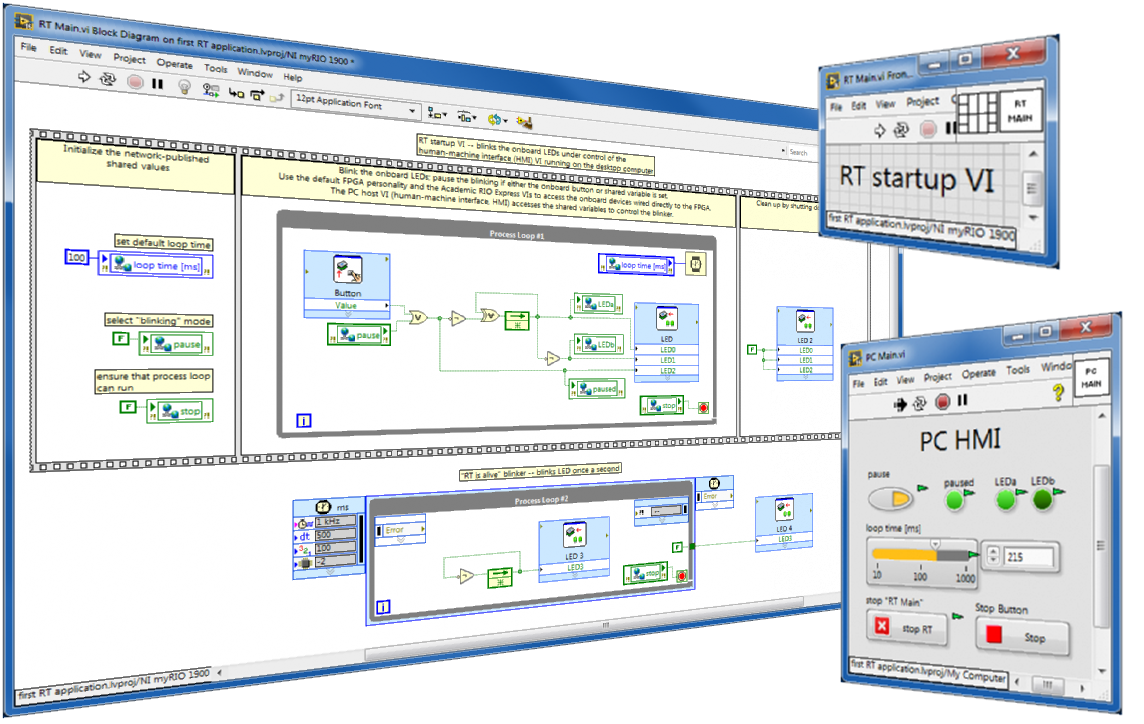
Make your first RT application
RT procedure
Follow along with this step-by-step tutorial to make a "hello, world!"-like application to experience the advantages of multiple linked VIs running simultaneously on the real-time (RT) target and desktop computer: (1) "RT Main" runs as the RT target start-up VI, blinks the onboard LEDs, and reads the onboard button; these onboard devices physically connect to the FPGA I/O pins which are accessed with the Academic RIO Device Toolkit Express VIs and default FPGA personality, and (2) "PC Main" VI runs on the desktop computer as a user-friendly human-machine interface (HMI) for remote command and control of "RT Main" through the network via shared variables hosted on the RT target.
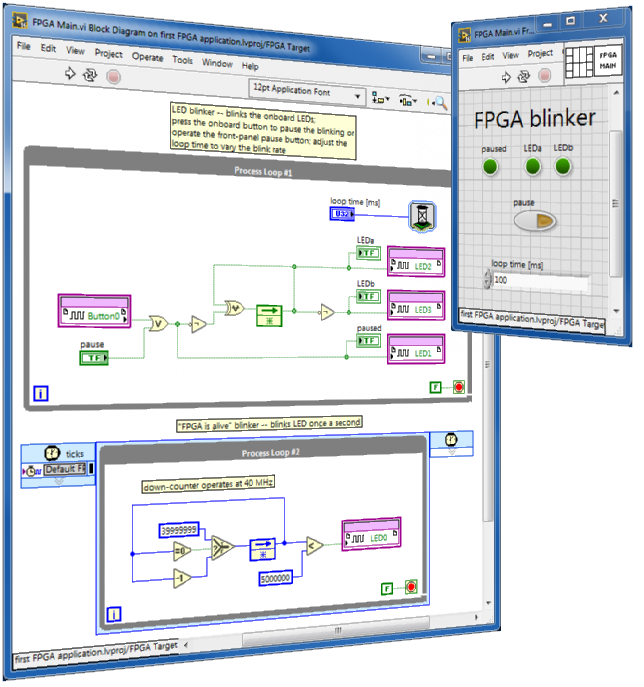
Make your first FPGA application
FPGA procedure
Follow along with this step-by-step tutorial to make a "hello, world!"-like application to experience the advantages of multiple linked VIs running simultaneously on the FPGA target, real-time (RT) target, and desktop computer: (1) "FPGA Main" VI blinks the onboard LEDs and reads the onboard button; these onboard devices physically connect to the FPGA I/O pins, (2) "FPGA testbench" VI runs on the desktop computer for interactive development and debugging of "FPGA Main" in simulation mode prior to compiling to a bitstream file, (3) "RT Main" VI runs as the RT target start-up VI; it runs "FPGA Main", interacts with its front-panel controls/indicators, and communicates with an external desktop computer via network-published shared variables, and (4) "PC Main" VI runs on the desktop computer as a user-friendly human-machine interface (HMI) for remote command and control of "FPGA Main" through the network.
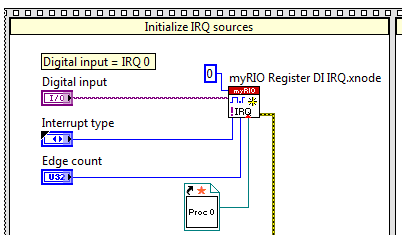
Run a callback VI each time that a digital input transition or an analog input voltage threshold crossing generates an interrupt request (IRQ).
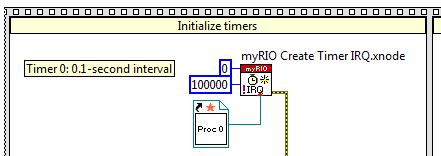
Run a callback VI each time that an FPGA-based interval timer generates an interrupt request (IRQ).
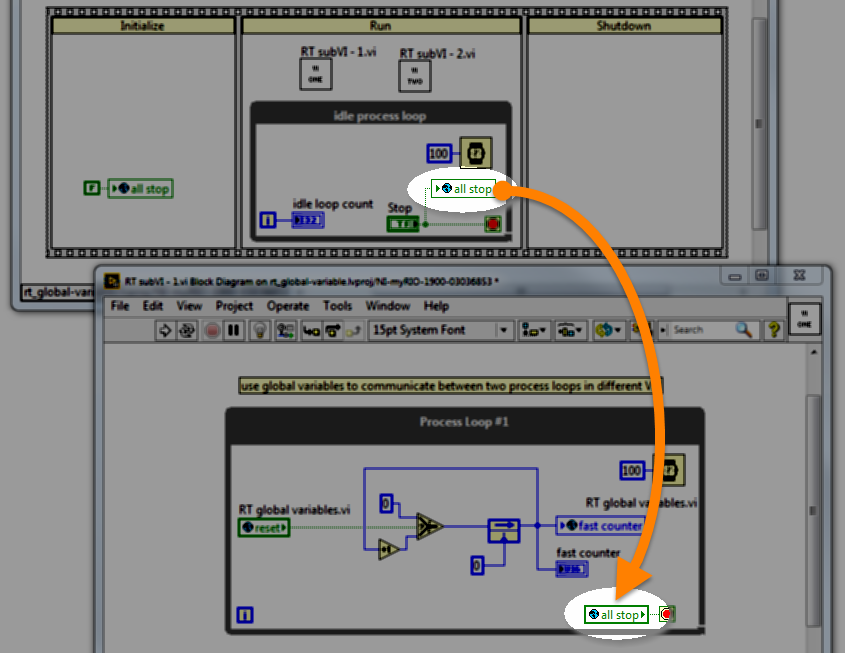
Global variable (RT)
RT code
Use a global variable to communicate between two parallel process loops contained within different VIs under the same target, and use a global variable to stop parallel loops with one "stop" button.
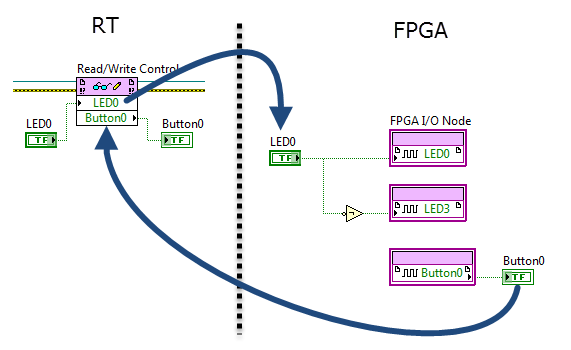
Programmatic front-panel communication with RT
FPGA code RT code
The RT VI operates (writes) the front-panel controls of the FPGA VI and reads its indicators.
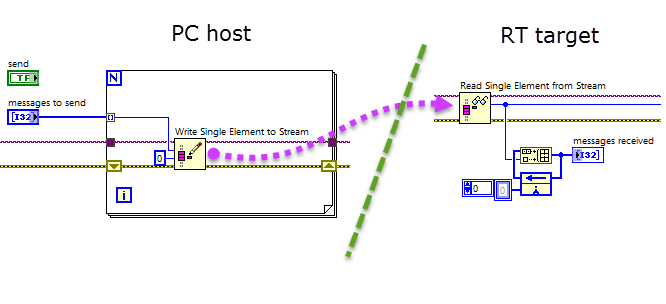
Send messages through a network stream channel
RT code PC code
Send command and status messages through a low-latency lossless network-based data communication channel between the RT target and PC host system.